Applications / zinc-nickel coatings
Thickness measurement of zinc-nickel coatings
Zinc-Nickel coatings consist of an alloy layer combining Zinc (typically 84-88%) and Nickel (12-16%). They are increasingly used for protecting steel-based parts again corrosion, using the sacrificial property of the zinc (being corroded prior to the base ferrous substrate) while the nickel slows down this very process.
Indeed, whereas standard zinc coatings resist only 96-120 hours to a salt spray test, the zinc-nickel coating can last more than 1000 hours. Moreover, zinc-nickel layers are more resistant to high temperatures over 120°C. On the other hand, they can also be an alternative to higher-end coatings like Cadmium plating who happen to be toxic and more expensive.
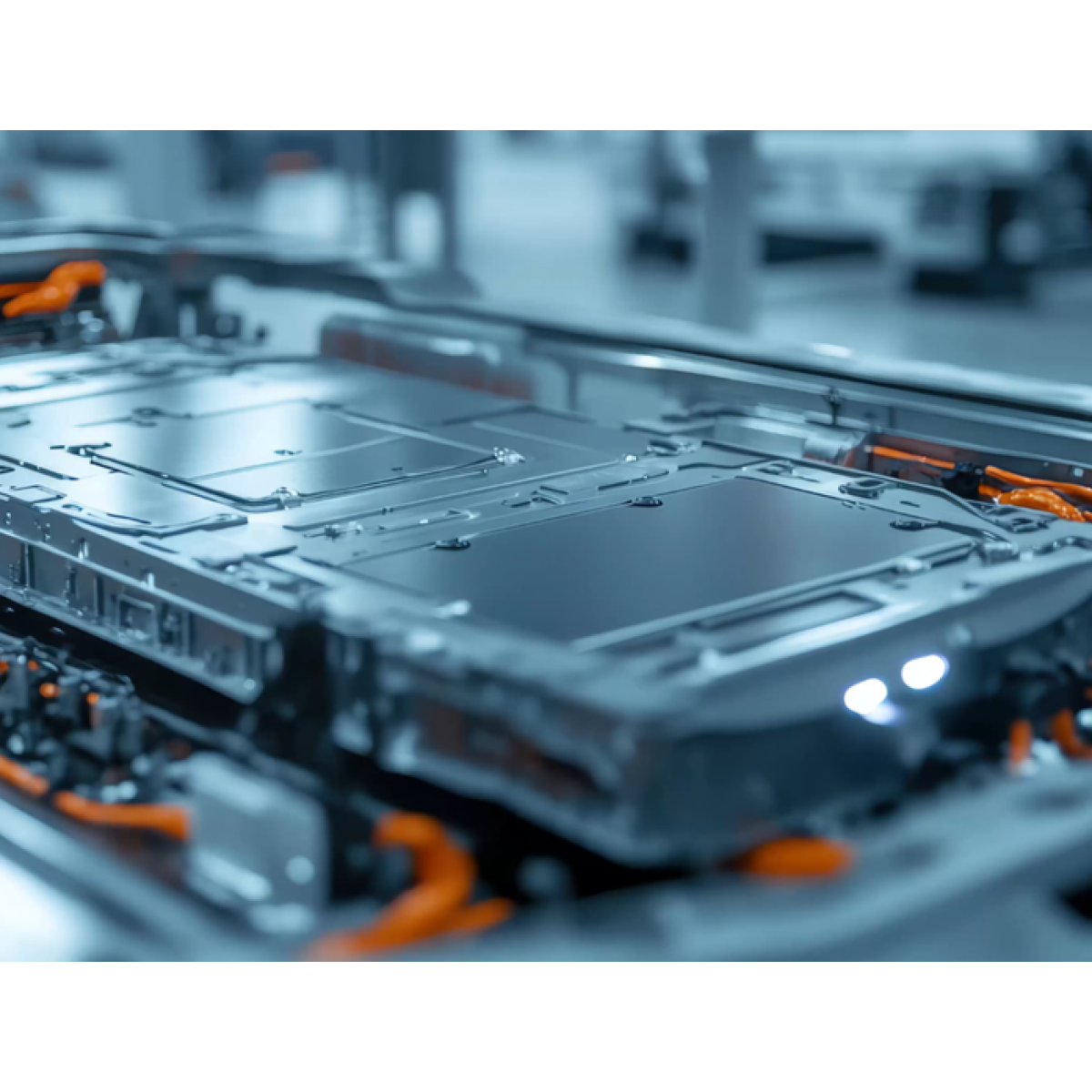
The automotive industry is one of the largest users of Zinc-Nickel coatings as it allows to reach long term protection against corrosion for parts that are exposed to the exterior environmental conditions or to high temperatures. Battery covers, brake systems (calipers and rotors) or fasteners are typically protected this way.
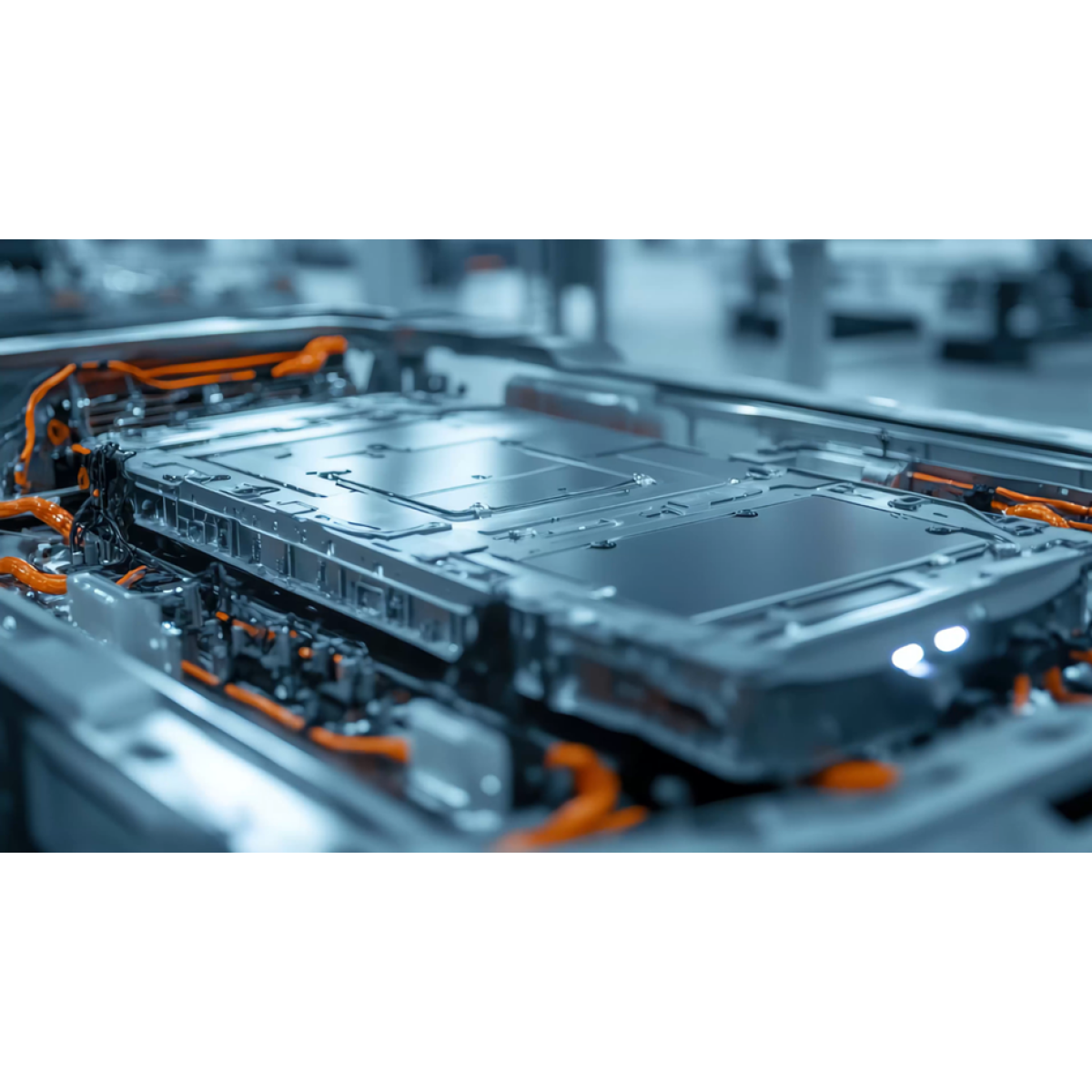
Battery cover protected with a ZnNi coating
In the aerospace industry, it is increasingly used as a non-toxic REACH compliant alternative to Cadmium coatings, for example on landing gear components, electrical connectors or fasteners (bolts, nuts and screws).
Why measuring the coating thickness is critical in such a complex process ?
ZnNi coatings are deposited through electroplating. The parts are plunged into a chemical bath containing Zinc and Nickel positive ions. Then a current is applied to the part, leading to the migration of the ions to the surface of the part and to their transformation into full Zinc and Nickel atoms within a coating layers generally ranging between 8 and 15µm.
However, when dealing for example with large battery covers, it is difficult to ensure that the electrical currents will be applied evenly on the whole surface, which will obviously lead to an inhomogeneous deposition of the coating. Moreover, when thinking about small parts like fasteners that are coated as batches within a rotating barrel, the uniformity of the deposition is even more difficult to reach.
Yet, the thickness of ZnNi coatings as well as its homogeneity is critical to ensure the corrosion protection while avoiding depositing too much and fragilize the coating itself while threatening the mechanical fitting of the part (especially for fasteners in threadings).
How to measure the thickness of Zinc-Nickel coatings ?
Besides destructive cross section microscopy and coulometric techniques, a range of non-destructive techniques are available for measuring the thickness of ZnNi coatings :
| Criteria | Enovasense Laser Photothermal | Magnetic induction probes | Handheld XRF | Benchtop XRF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement principle | Thermal diffusion response | Magnetic field response | X-ray fluorescence of the coating | X-ray fluorescence of the coating |
| Contact and distance | Non contact (40mm distance with +/- 3mm tolerance) | Contact | Near contact | Non contact (20mm distance with +/- 0.1-0.5mm tolerance) |
| Measuring time | 1 second | 1 second | 5-30 seconds depending on requested accuracy | 15-20 seconds |
| Operator impact | Independent of operator | Operator dependent (how the contact is applied) | Operator dependent | Low operator dependency |
| Calibration | No recalibration needed | Needs regular recalibration | Drifts in time, regular recalibration needed | Drifts in time, regular recalibration needed |
| Size, shape and edge dependency | Independent of shape, curvature or geometry. 1mm spot size without edge effect | Shape dependent. Not working close to edges and holes | Shape dependent. 3-8mm spot size that cannot handle smaller parts | Shape dependent. 0.1-0.3mm spot size for small areas but not working close to edges/holes |
| Automation | Can be automated (e.g., embedding probe on a robotic arm) | Hand-held device | Hand-held device | Benchtop device |
The Enovasense laser photothermal technology allows a faster and more stable measurement, with lower dependency to distance and part geometry. It is also an ideal choice for in-line integration.
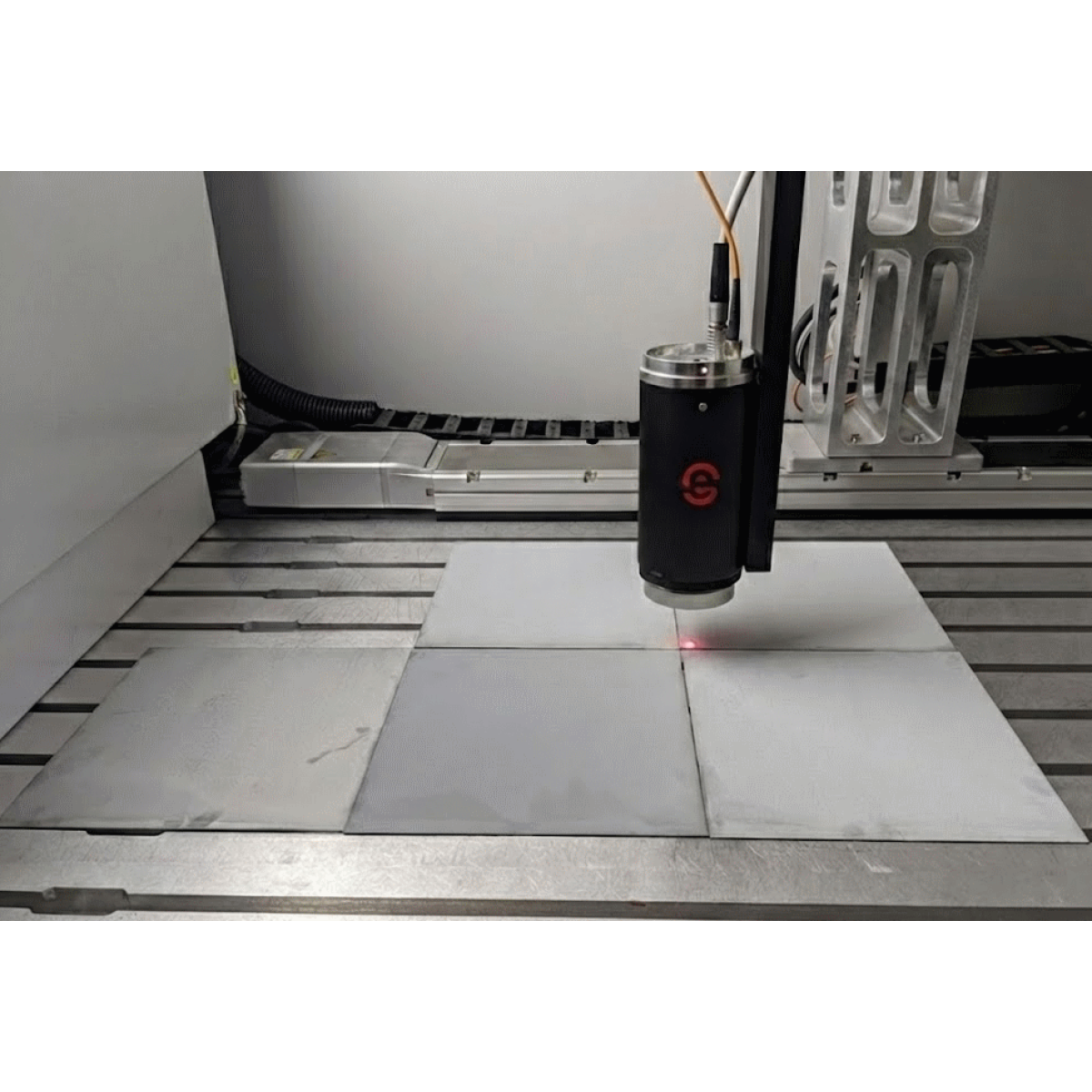
Zinc-Nickel coating thickness measurement with an Enovasense sensor
How Enovasense performs on ZnNi coatings
Regarding the accuracy of the measurement, Enovasense performed test on samples that showed various thickness levels covering the whole range of the tolerance interval, between 10 and 30µm. Those measurements were then compared with magnetic induction measurements.
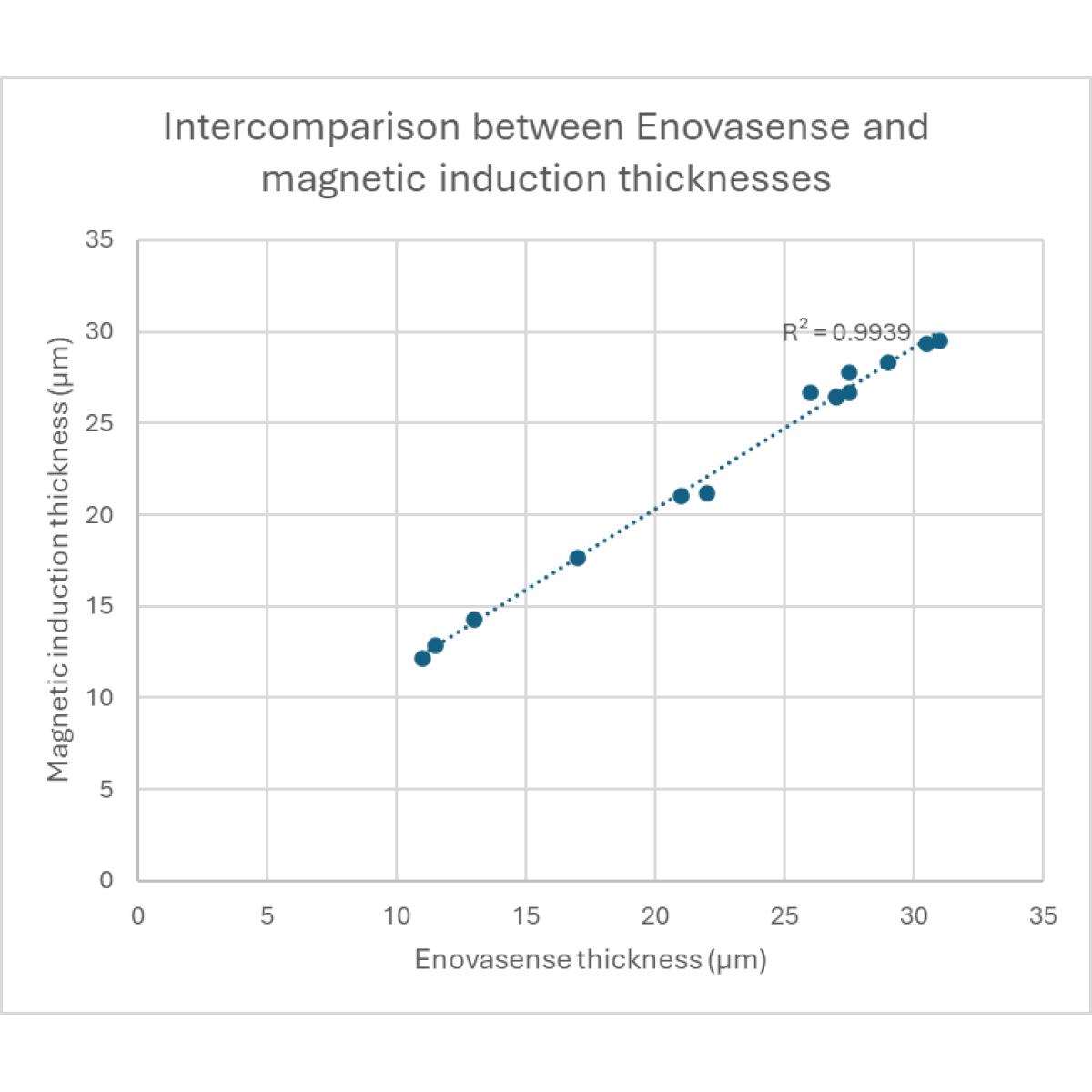
We observe that the Enovasense sensor highly correlates with the magnetic induction values.
We then performed a type 1 MSA study on a sample of 41µm, quite in the middle of the range of interest.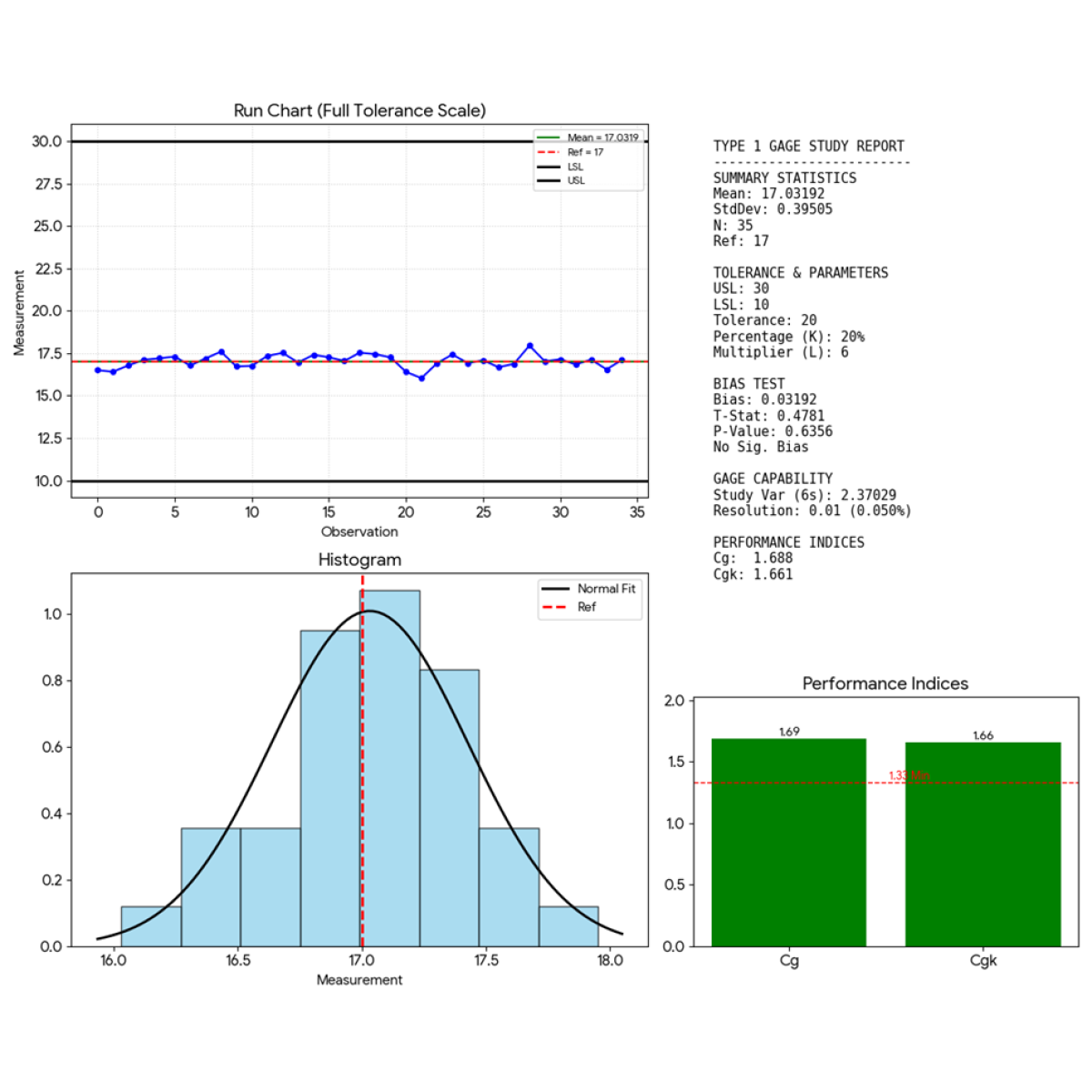
• Bias: The P-Value (0.6356) is higher than the standard alpha level of 0.05. Therefore, the bias is not statistically significant. The measurement system is accurate relative to the reference.
• Capability : Both Cg (1.69) and Cgk (1.66) exceed the standard threshold of 1.33. This indicates that the measurement system is capable. The variation is acceptably small compared to the allocated tolerance.
Finally, for this application, the impact of the measurement distance and measurement angle was tested. We found that the sensor was able to stay within a +/-3µm range when varying the distance from 15 to 25µm (with a nominal distance at 20µm) as well as when varying the angle of approach from -40° to +40° (with a nominal angle at 0°).
How to integrate Enovasense sensors for controlling such coatings
The Enovasense probes are compact and lightweighted which allows to imagine various integration possibilities :
Robotic integration or fixed positionning

The very compact Enovasense probe can be implemented on a robotic arm and then automatically control various positions of the part to measure.
For large parts like battery covers, the parts can be brought by a robotic arm to the sensors that are in a fix position.
Offline control station

The HKL2 control station allows to perform thickness mapping and cycles of movements and measurements in order to automatically measure various positions on the part. For smaller parts (like fasteners), it can also measure automatically batches of parts.